How is Metrology Used in Manufacturing and Engineering?
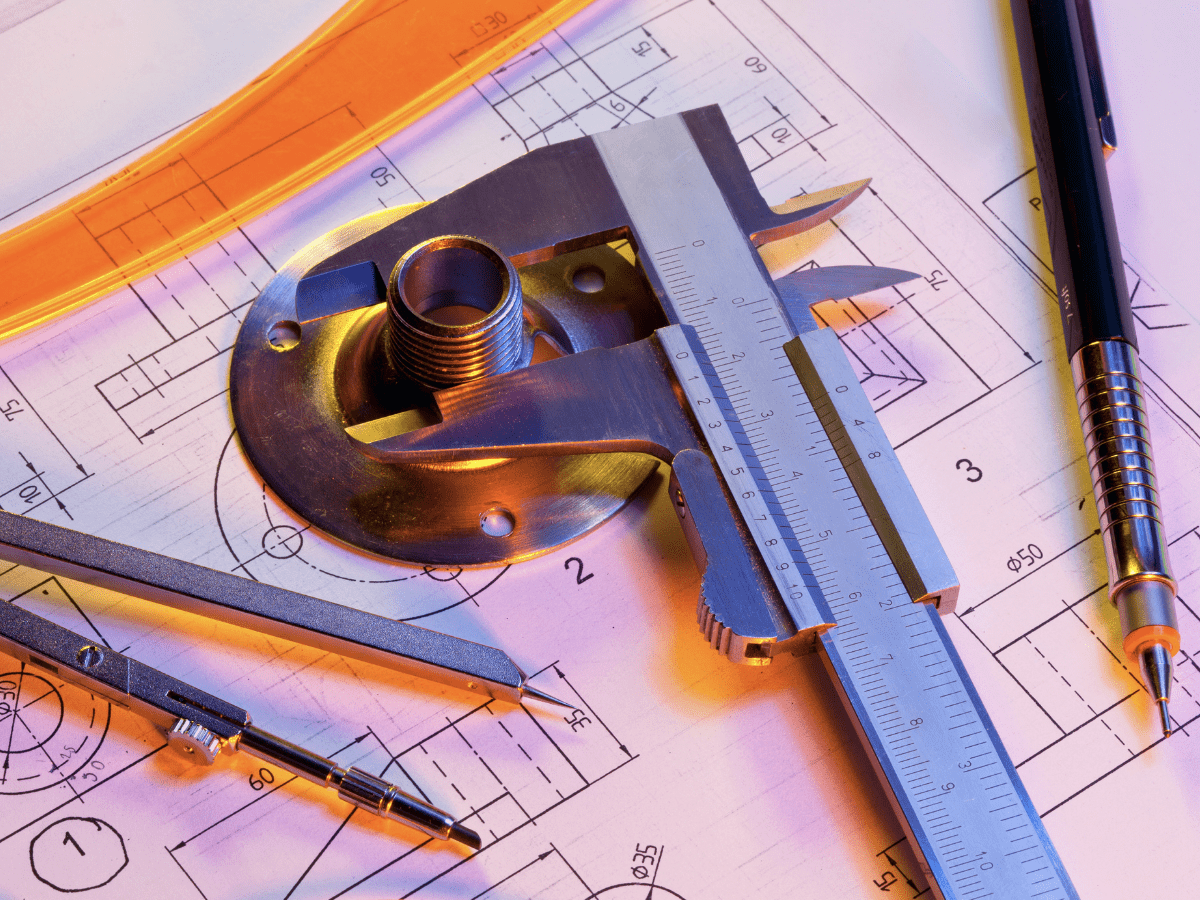
When manufacturing and inspecting thousands of parts, it is important to control your manufacturing process to ensure that it is capable of repeatedly creating parts that conform to the desired tolerance. In general, the tighter the tolerance, the less capable a specific process will be.
Determining the capability of a process is one of many important duties involved in the world of metrology, which improves overall quality assurance and dependability in manufacturing.
In manufacturing, the term “metrology” is generally used when referring to quality inspection, such as manual layout inspection, as well as coordinate measuring machine inspection. More specifically, metrology in manufacturing is the study of how to reliably measure and manufacture a product.
The term metrology is much broader than just inspection; but in general, when you hear metrology in manufacturing that is what people are referring to. There are so many intricacies involved with metrology that many textbooks have been filled with explanations of what metrology means and how to apply the concepts of metrology.
What Is The Origin Of The Word Metrology?
The etymology of the word metrology derives from the Greek “metron” plus “logy,” which literally translates as the “study of measurement”. The word metrology is a very broad definition that encompasses many disciplines within the world of manufacturing, such as engineering inspection, and calibration.
One of the oldest systems of weight and measurements, metrology was originally established using the human body as a scale. This is where we get the terms “foot” and “cubit”. This was an inaccurate scale of measurement because not everyone has the same size foot or the same length of limbs. Regardless, these measurements were used for thousands of years for building structures and for making trades.
With modern technology, metrology has become far more refined and advanced. We now have standards of measurement that define exactly what a foot and a meter is. We also have far more accurate methods for measuring items compared to the standard units.
What Are The Uses Of Metrology In Manufacturing?
There are specific roles in manufacturing that use metrology in their day-to-day duties, and some roles that will never need the principles of metrology to perform their duties.
Metrology in Engineering
Metrology is used by engineers in manufacturing to define and establish datums and tolerances on blueprints for inspection. Metrology is also used by engineers when creating tooling and fixtures that aid in the inspection of a product.
Design engineers use capable process tolerance plus geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GDT) to apply tolerances to a blueprint. This then serves as a guide to determine the best way to manufacture and inspect a product.
If applied correctly, GDT can dramatically improve the function of a part and decrease inspection time. If applied incorrectly, GDT can cause a part to not properly fit its mating components.
Metrology in Manufacturing
Manufacturing is dependent on the tolerances produced by engineering to better determine the best way to proceed when creating a product. If a feature has a very tight tolerance, this will prompt manufacturing to design a strategy that will be capable of producing a product that will conform to the tolerances.
Manufacturing will typically not use the same strategy on a ±.001 inches tolerance that they would on a ±.100 tolerance. A tight tolerance requires extra attention in the manufacturing process.
By acknowledging the tighter tolerance features, manufacturers can prepare for, and hopefully avoid, future roadblocks that might come up when producing a product.
Metrology in Quality Inspection
Quality inspection executes the best practices of metrology by actually physically inspecting and validating that a product conforms to its blueprint and other respective specifications. Quality inspection also typically works with the engineer to resolve any illegal applications of GDT and datum definition.
Quality inspection in manufacturing is typically performed with the aid of calibrated equipment such as calipers, micrometers, height gages, optical comparators, and coordinate measuring machines.
A quality inspector may use formulas to properly apply measurements to GDT, as well as to study the capability of a process
Quality inspection must ensure that a part conforms to the blueprint and other pertaining specifications. Quality inspection is responsible for identifying non-conforming features and aiding manufacturing in finding solutions.
Metrology in Quality Management Systems
Quality management systems use metrology studies to best determine the correct procedures for determining the sample size of a particular product, as well as the best practices for inspecting a product.
The quality management system can also be used to ensure that the correct tools are used when inspecting products. For example, you would not want to use a tape measure for a ±.001 inches tolerance. Instead, it is better to use an instrument that is able to measure 10x the resolution of the tolerance, such as a micrometer that has the resolution of .0001 inches.
Metrology in Process Capability
Metrology is used in process capability as a warning sign for manufacturers that they are potentially going to have failing parts, depending on how much of the tolerance on a feature that they are currently using.
The most commonly used tool for calculating process capability is CPK (Process capability) and PPK (process performance). CPK is used for processes that are actively being controlled by the statistical capability; and PPK is used for processes that are already complete and are simply being scrutinized by the process capability.
Metrology in Calibration
Metrology is used in calibration to ensure that a tool is capable of repeatedly measuring to the tool’s manufacturer-designed resolution. It is the duty of the calibration provider to identify if a tool is not working properly. And, in some cases, the calibration house is also capable of repairing damaged and broken tooling.
Calibration labs typically can calibrate a large variety of tools that are at different measurement resolutions.
Conclusion
Metrology plays a crucial role in creating functional products. Without the use of metrology in manufacturing, large assemblies such as automobiles or airplanes would likely never assemble reliably. And without process capability, we would not be able to determine if a process is capable of continually making a product without failures.
If you have any upcoming inspection or CMM programming needs, please contact us.




